loads used in rockwell hardness test|rockwell hardness scale chart : dealer Hardness Conversion for Rockwell B Scale or Low Hardness Range. Find the . WEB14 de jul. de 2022 · The live casino is – genuinely – a lot of fun to play. The entry-level stakes are also considerably lower than Las Vegas. You can also just lurk and watch the .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 22 de mai. de 2014 · Cruzeiro Esporte Clube. All information about Cruzeiro (Série A) current squad with market values transfers rumours player stats fixtures news.
Preliminary test loads (preloads) range from 3 kgf (used in the “Superficial” Rockwell scale) to 10 kgf (used in the “Regular” Rockwell scale). Total test forces range from 15kgf to 150 kgf (superficial and regular) to 500 to 3000 kgf (macrohardness).
charpy impact test are used to help determine a metals:
The Vickers hardness test method, also referred to as a microhardness test .The type of material and expected hardness will determine test method. Materials .The Brinell hardness test method as used to determine Brinell hardness, is defined in .
Hardness Conversion for Rockwell B Scale or Low Hardness Range. Find the .The characteristics of case hardening are primarily determined by surface .Consequently, it can be used on very thin materials. In a Knoop test, a .
The Rockwell scale is a hardness scale based on indentation .
In regular Rockwell testing the minor load is always 10 kgf (kilograms of force). The major load can be any of the following loads: 60 kgf, 100 kgf or 150 kgf. No Rockwell hardness value is .
The Rockwell hardness test utilizes 1 of 6 different main loads: In total, this gives 30 different Rockwell scales. Each one is characterized by a different combination of indenter type and main load, and is suitable for a particular material or .
The Rockwell hardness test measures hardness in progressive numbers on different scales corresponding to the size of ball indentor used; scale symbols correspond to the loads of 60 .There are two general classes of Rockwell test: Rockwell and superficial Rockwell. In Rockwell testing, the minor load is 10 kgf and the major load is 60, 100 or 150 kgf. In. Every Rockwell hardness scale is identified by a letter signifying the indenter type and the two loads used for the test. A Rockwell hardness number is a combination of the numerical hardness value and the letter for .
The Rockwell hardness test measures the depth of penetra-tion of an indenter into a material under a known load. It provides a hardness value based on the depth of penetration. 2 Brinell . There are two types of Rockwell test (Table 23.1): Rockwell: the minor load is 10 kgf, the major load is 60, 100, or 150 kgf. Superficial Rockwell: the minor load is 3 kgf and major loads are 15, 30, or 45 kgf. Table 23.1: Some .
These indenters are unique to the Rockwell hardness test alone. Test Load – The range of loads and the combination of initial minor loads and final major loads also distinguishes the Rockwell method from other test methods. The applied load ranges from 15kgf to 150kgf, where a 3kgf is usually the minor load before applying the major loads. .During the preliminary test, the pre-load force is held for a specified dwell time to create a baseline depth of indentation (h o). The applied preload breaks through the surface by reducing the effects of surface finish. . The Rockwell .Metals with high Rockwell hardness are resistant to wear and can be used in applications with high loads. The Rockwell Hardness Test is the most accurate method of measuring the hardness of a material, and it is easier to perform than the Brinell or Vickers tests.01. II. Theory and Principle of the Rockwell Hardness TestRockwell hardness test using Rockwell hardness scale is one of the extensively used and accurate hardness test methods prevalent in industries for thin steel, lead, brass, zinc, aluminum, cemented carbides, iron, titanium, copper alloys, and certain plastics. . Regular Rockwell Hardness Test where the minor load is 10 kgf and major load is 60 .
Figure: Rockwell hardness test procedure. The actual test load F 1 is applied in addition to the preload and the indetor penetrates the material with the total force F=F 0 +F1. The test load to be set is taken from table books depending on the indenter and the material to be tested. . The advantage of Rockwell hardness testing is the .
Hardness test methods in the macro range include Brinell, Vickers and Rockwell. Hardness testing in the low-load range applies when the test load falls between an interval of 0.2 kgf and 5 kgf (test load ≥ 0.2 kgf and < 5 kgf). The most commonly used low-load method is Vickers. Low-load hardness testing is mainly used for testing of small .
rockwell hardness testing chart
The Rockwell hardness test method, as properly defined in ASTM E-18 standards, is the most commonly used hardness test method among all the other methods. . This range of loads is often applicable for both superficial and normal Rockwell scales. For the total test loads required, this can also range from 15kgf to 150kgf and can sometimes be .A widely used variant of the Rockwell hardness test is the superficial Rockwell test, wherein the minor load is 3 N and the major loads are 15, 30, or 45 N.Further details on the Rockwell superficial hardness scales are available in the relevant ASTM standards (ASTM 1984).The Rockwell hardness values are expressed as a combination of hardness number and a scale . Rockwell hardness testing methods are defined in the following standards: ASTM E18 Metals, ISO 6508 Metals, . There are two types of Rockwell test (Table 23.1): Rockwell: the minor load is 10 kgf, the major load is 60, 100, or 150 kgf. Superficial Rockwell: the minor load is 3 kgf and major loads are 15, 30, or 45 kgf. .
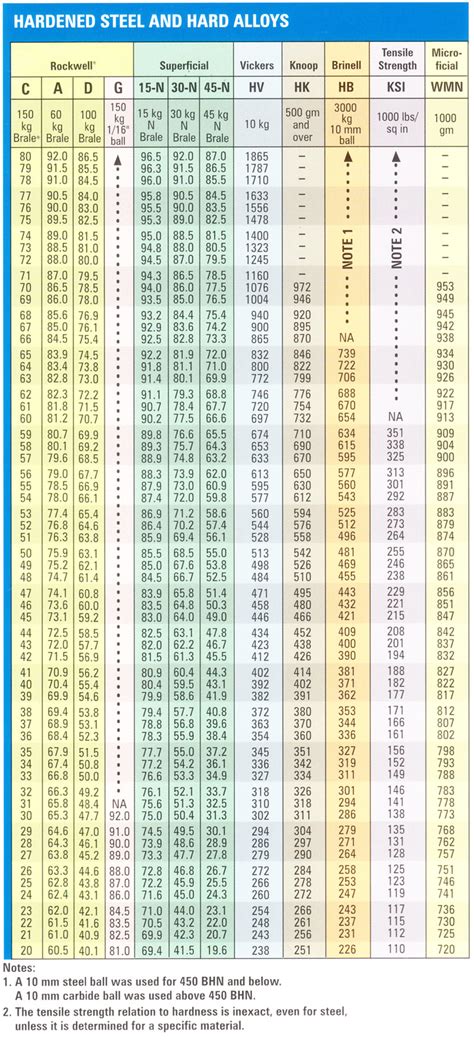
Every Rockwell hardness scale is identified by a letter signifying the indenter type and the two loads used for the test. A Rockwell hardness number is a combination of the numerical hardness value and the letter for the scale preceded by the letters, HR. For instance, a hardness value of 80 on the Rockwell A scale is denoted as 80 HRA. .In Rockwell testing, hardness is determined by measuring the comparative depth of two carefully controlled indentations, one superimposed over the other. . Rockwell scale, the Minor Load is is 10 kgf and the Major Load may be 60, 100, or 150 kgf. In the superficial scale (S), the Minor Load is 3 kgf and the Major Load may be 15, 30, or 45 kgfLoad: The Rockwell hardness test uses a pre-load of 10 kgf, followed by the application of the main load, which varies depending on the Rockwell scale being used (e.g., 60 kgf for the Rockwell A scale, 150 kgf for the Rockwell C scale). The load is applied for a .The Rockwell hardness test method, as defined in ASTM E-18, is the most commonly used hardness test method . Preliminary test loads (preloads) range from 3 kgf (used in the "Superficial" Rockwell scale) to 10 kgf (used in the "Regular" Rockwell scale). Total test forces range from 15 kgf to 150 kgf (superficial and regular) to 500 to 3000 kgf .
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Theauthorwouldliketothankthefollowingpersonsforsharingtheir experienceandprovidinginformationforthisGuide.Theirinputandreview .
The Rockwell hardness test method has a whopping 30 hardness scales defined by the indenter and the two loads. A Rockwell hardness value is a combination of the numerical hardness number and the Rockwell hardness . Variants on the Rockwell hardness test procedure are used depending on the material and strength of a part. The most common Rockwell variants include: HRC – Known as “Rockwell C,” a 150 kgf load is applied via .
The Rockwell Hardness Test is one of several tests used to determine whether a material is solid and durable enough to be employed as a component of an object. The Knoop, Brinell, and Vickers procedures are additional . Rockwell hardness testing can determine the hardness of most metals, alloys and plastics. . • Regular Rockwell: the minor load is 10 kilograms of force (kgf) and the major load is 60, 100 or 150 kgf. • Superficial Rockwell: the minor load is .
The Rockwell Hardness Test is actually one of several tests aimed to gauge a material’s compatibility as a component to an object based on their strength and durability. The other tests in the series include the the Knoop, Brinell, and Vickers methods. . Some variations of the test would require that the major load remain on the material .Each Rockwell hardness scale is identified by a letter designation indicative of the indenter type and the major and minor loads used for the test. The Rockwell hardness number is expressed as a combination of the measured numerical hardness .
The equation for the Rockwell hardness test for metals is below: d=depth from zero load point. N and s = various scale factors that can be found in the chart below. . There are other scales that are associated with a Rockwell superficial test. These scales use a lighter loads and shallow impressions to perform the test. These are used on .3.2 Conducting the Test. Positioning the Sample: Secure the material sample in the testing machine.; Selecting the Indenter: Choose the appropriate ball diameter based on the material hardness.; Applying the Load: Gradually apply the specified load using the machine.The load should be maintained for a predetermined dwell time, usually between 10 to 15 seconds.In the Rockwell hardness test, the indenter creates a hardmetal ball or diamond pyramid-shaped indentation, depending on the type of indenter used. The depth of penetration is measured, allowing for hardness evaluation. . On the other hand, Vickers hardness testing typically uses lower loads, making it suitable for smaller and more delicate .
Each Rockwell hardness scale is identified by a letter designation indicative of the indenter type and the major and minor loads used for the test. The Rockwell hardness number is expressed as a combination of the measured numerical hardness . The Rockwell hardness test involves applying a sequence of loads to the material and measuring the depth of the resulting indentation, which indicates the material’s hardness. . The major load can range from 60 to 150 kgf, depending on the specific Rockwell scale being used. This load creates a deeper indentation in the material. Hold the load.
In the Rockwell hardness testing, the indenter applies the first load to the test piece. The indent is then measured, and the value obtained is used for the base calculations. This first load is removed, and another heavier load is applied to the indenter on the test piece. . HR is the abbreviation for Rockwell hardness. C represents a load . The choice is not only between the regular hardness test and superficial hardness test, with three different major loads for each, but also between the diamond indenter and the 1/16, 1/8, 1/4 and 1/2 in. diameter steel ball indenters.
rockwell hardness tester diagram
UDM Processing Services LTD., registration number НЕ 435747, а company organized .
loads used in rockwell hardness test|rockwell hardness scale chart